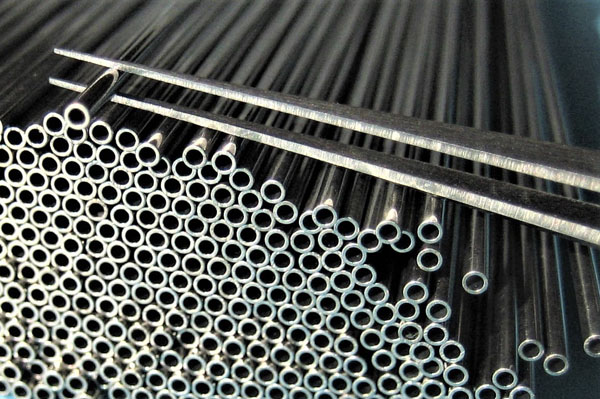
Hypodermic Tube
Precision Mandrels, Wires and Tube Components for Medical Devices
Stainless steel precision tube is manufactured by two different means; seamless tube is drawn down to size from a larger diameter starting tube, whereas welded tube uses rolled stainless steel strip as starting material. The strip is formed into a hollow tube shape, then longitudinally welded along the join between the meeting edges. Both seamless tube and welded tubes are drawn through a die, annealed, redrawn, then re-annealed several times in order to reach the desired dimensional and mechanical properties.


Stainless Steel & Nitinol Tube
We supply both seamless tube and welded redrawn stainless steel tube. Seamless tube is particularly useful when extremely thin walled tubes are required as there is no weld present. Wall thickness as small as 0.050mm (0.002”) can be achieved; even for those in excess of 20mm diameter. Thin wall tubes are used where space or weight is at a premium, such as instrument cases, precision probes, minimally invasive instrument casings, and endoscopic probes. These can all take advantage of thin wall seamless stainless steel tubes. Thin wall tubes are also used for their superior thermal conductivity across a thin wall.
The superelasticity of nitinol confers an advantage in many invasive medical device applications. Nitinol can be laser cut and welded under certain conditions to reduce embrittlement.


Thin Wall Tube
Thin wall tubular mandrels permit faster cooling of the substrate polymer than wire mandrels. Tubes can be swaged, centreless ground or profile ground. Shaped tubes (square, rectangular, oval etc.) can also be supplied, allowing for highly flexible outcomes in the interior shape of the polymer product made by our customers. We can also join tubes together by laser welding or vacuum brazing, and we can laser weld end plugs or machined parts to hypodermic tubes. Parts are often then coated in low friction parylene or with PTFE.
Careful selection of tube dimensions and materials are important to maintain biocompatibility with strength whilst allowing sufficient space in the tube bore to house wires and instruments. Austenitic stainless steel tubes provide an economic yet strong and biocompatible solution for design engineers in the medical device industry to specify sheaths around both actuators and sensors which are used in keyhole surgery. Thin-wall stainless steel hypotube is sufficiently strong and flexible to act as a crimp in holding together wire pairs. Radio-opaque marker bands, used to locate or “mark” the position of X-ray transparent polymer catheters, are made from platinum iridium tube, tantalum tube and gold hypotube.
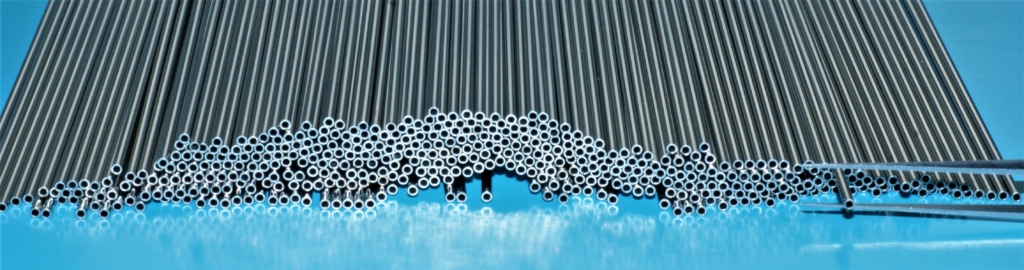
Stainless Steel Hypotube
Thick wall stainless steel hypotube (or capillary tube) is useful for narrow gauge, rigid stainless steel hypotube assemblies. We manufacture a wide range of stainless steel hypodermic tube components and assemblies. Many of these products are used to deliver active pharmaceuticals and medical instruments to the site of surgery, or for other remotely activated tasks. Speciality needles, biopsy instruments, catheter assemblies and remotely driven medical robotic instruments all use precision stainless steel hypotubes. Gas detectors, gas probes, and needles all require a strong stainless steel hypotube to be incorporated into an assembly. Our laser welding capability provides clean joints between a hub or fitting to the proximal end of the hypotube and also facilitates a strong join between the distal end of a hypotube and the end fitting, probe or activator.
Nitinol tube
When superior flexibility is required, superelastic nitinol can be incorporated into the tube assembly or mandrel. Although joining nitinol tube to fittings made from dissimilar materials such as stainless steels can pose challenges, techniques involving specialist welding, brazing, crimping or adhesive are employed depending on the precise application.
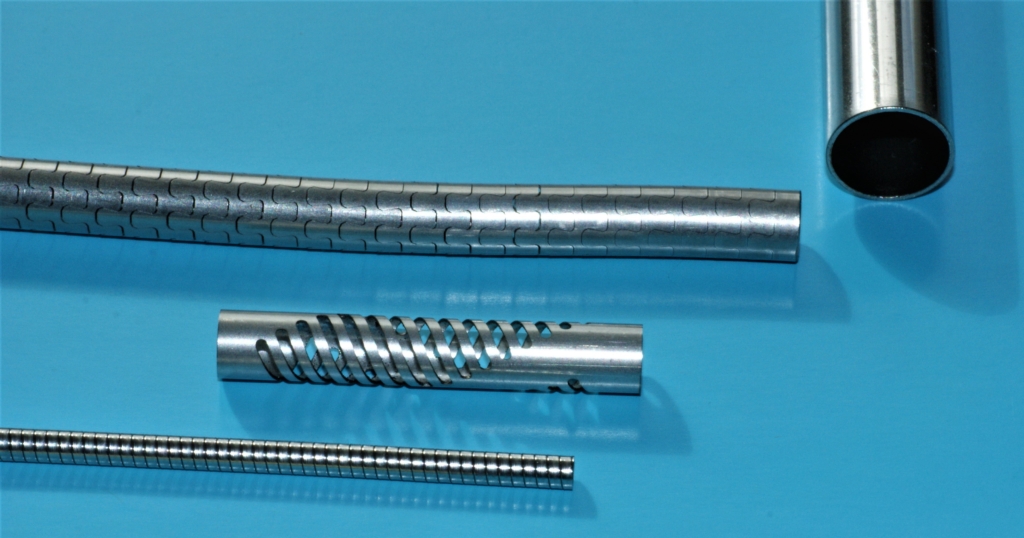


Laser cut hypotubes
Laser cut hypotubes made from nitinol, 316 grade stainless steel or 304 grade stainless steel are used in a wide variety of medical devices including catheter mandrel assemblies. Laser cutting hypotubes is used to confer additional flexibility to a tube in order that it can find its way, often by creating a steerable device, to the active site.
In some applications, sensors located at an active site deliver output back to the surgeon. Again, superelastic nitinol is sometimes specified as an alternative to austenitic grades (AISI304, 316, 302 or 321) where elasticity and the tube returning to its original configuration, is needed.


Abrasive Tube Cutting and EDM Tube Cutting
Thicker tube walls, above 0.5mm, are more conducive to either abrasive disk cutting or electro-erosive cutting methods than for laser cutting. Tubes are deburred and polished to achieve a superior surface finish.
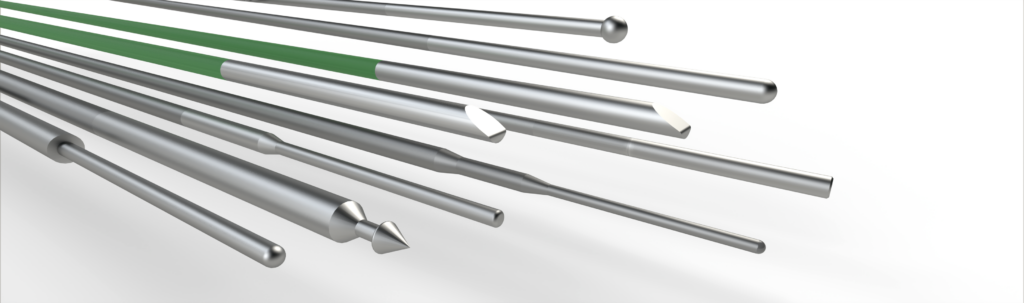
Mandrels
We make mandrels from stainless steel and nitinol precision tube and wire. These are in turn used to develop and produce sophisticated catheters for interventional and other medical device applications.
Thin wall tubular mandrels permit faster cooling of the substrate polymer than wire mandrels. Tubes can be swaged, centreless ground or profile ground. Square thin wall tubes, rectangular tubes, oval tubes and other shaped thin wall tubes can also be supplied, allowing for highly flexible outcomes in the interior shape of the polymer product made by our customers. We can also join tubes together by laser welding or vacuum brazing, and we can laser weld end plugs or machined parts to hypodermic tubes. Parts are often then coated with parylene or PTFE to confer lubricity.
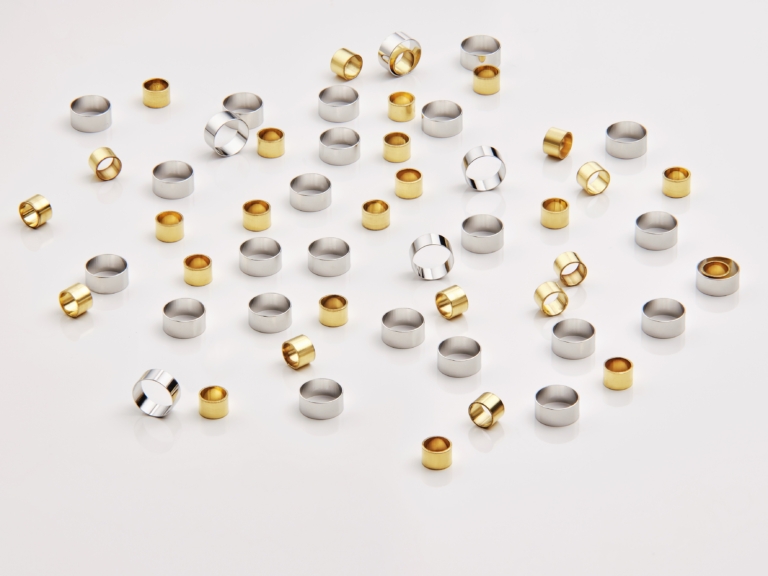

Marker bands, Ring electrodes
We offer custom-made radio-opaque marker bands, used to locate or “mark” the position of X-ray transparent polymer catheters. Our marker bands are made from platinum, platinum-iridium, tantalum tube and gold hypotube. Inside diameters from 0.0045” (0.11mm) to 0.5” (12.7mm) are available in these materials.
We carry an extensive range of stock sizes in platinum (99.95% purity) and platinum 10% iridium alloy.
We also manufacture Ring electrodes and other specialist hypotubes to customers for the manufacture of EP Ring electrode assemblies, catheter shafts, and other medical device sub-assemblies.
Crimps, spacers
Thin-wall stainless steel hypotube is sufficiently strong and flexible to act as a crimp in holding together wire pairs. Spacers are made from tubes which are cut to precise short lengths. Tube cutting by use of an abrasive wheel and laser cutting hypotubes are used, followed by deburring and other surface treatment such as electropolishing or passivation if required.
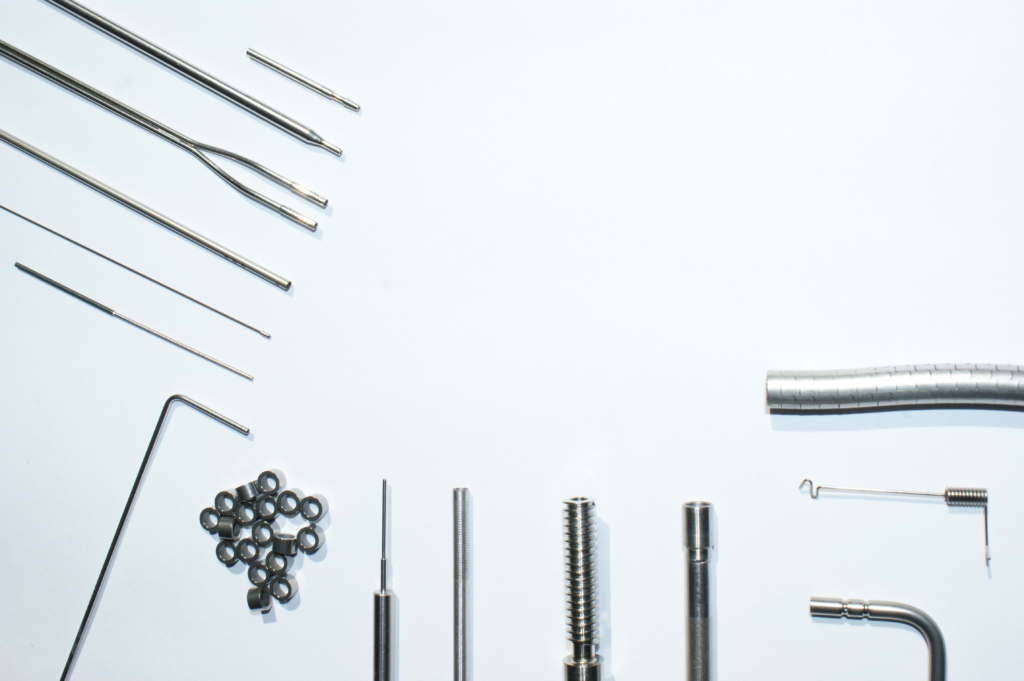

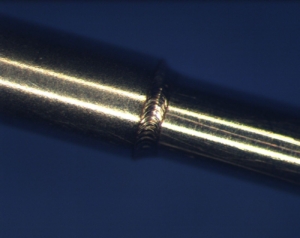
Laser welded hypotube assemblies
We manufacture a wide range of hypodermic tube components and assemblies using laser welding. Many of these products are used to deliver active pharmaceuticals and medical instruments to the site of surgery or for other remotely activated tasks. For example. speciality needles, biopsy instruments, remotely driven medical robotic instruments all incorporate precision stainless steel tubes and can be securely attached to wires, fittings and fixtures by the careful use of precision laser welding.
Tube facts and figures
Our tube possibilities comprise the following:
Materials: The majority of our products incorporate austenitic stainless steel grades AISI 302, 304, 304V, 316, and nitinol.
We also offer titanium, copper, brass, platinum and gold alloys, nickel alloys including Inconel, Kovar, Hastelloy and Monel.
Marker bands from platinum-iridium, tantalum and gold tubes made by laser cutting hypotubes in these exotic metals
Outside diameters from .012” to 1.20”
Wall thicknesses from 0.003” upwards